TL;DR It’s common to include interactive Python sessions inside documentation. With a small script we can turn these docs into Jupyter notebooks and serve them instantly.
Example docs:
Mac/Linux
git clone https://github.com/houbie/tomlkit.git && cd tomlkit &&./pw run-docsWindows
git clone https://github.com/houbie/tomlkit.git && cd tomlkit && pw run-docs
Exploring a library
I was recently exploring tomlkit, a library for parsing and editing toml files.
It would have been nice if the docs where a Jupyter notebook that you can play with interactively. No more copy/paste to the REPL.
Of course this only makes sense if the effort for starting the notebook is less than a dozen copy/pastes.
The conversion script
The built-in doctest makes it trivial to separate text and code
from doctest import DocTestParser
with open(src, "r") as md:
docs = DocTestParser().parse(md.read())
for part in docs:
if isinstance(part, Example):
# Example contains source and wanted output
source = part.source
...
else:
# plain (markdown) text
source = part
...
The documentation parts can then be stored in notebook cells, a list of dicts that is dumped as json to get the final notebook.
So:
Modifying
---------
TOML Kit provides an intuitive API to modify TOML documents::
>>> from tomlkit import dumps
>>> from tomlkit import parse
>>> from tomlkit import table
is converted to:
[
{
"cell_type": "markdown",
"source": [
"Modifying\n",
"---------\n",
"TOML Kit provides an intuitive API to modify TOML documents::\n"
]
},
{
"cell_type": "code",
"source": [
"from tomlkit import dumps\n",
"from tomlkit import parse\n",
"from tomlkit import table\n"
]
}
]
Launching the Jupyter server
We still need to avoid that our potential users give up when confronted with too long or too complex instructions.
This is where pyprojectx comes into play; we’ll use it to start the entire experimentation session with a oneliner:
git clone https://github.com/houbie/tomlkit.git && cd tomlkit &&./pw run-docs
The run-docs alias is configured in pyproject.toml:
[tool.pyprojectx]
jupyter = """\
jupyter
.
"""
[tool.pyprojectx.aliases]
run-docs = "python docs/md2notebook.py && pw@jupyter notebook --notebook-dir=docs"
Jupyter and the project dir (current dir) are added to the tool.pyprojectx section in pyproject.toml, making them both available in an isolated virtual environment (no impact on project dependencies).
The run-docs alias runs the conversion script and launches the Jupyter server.
When we open quickstart.ipynb we can start fiddling.
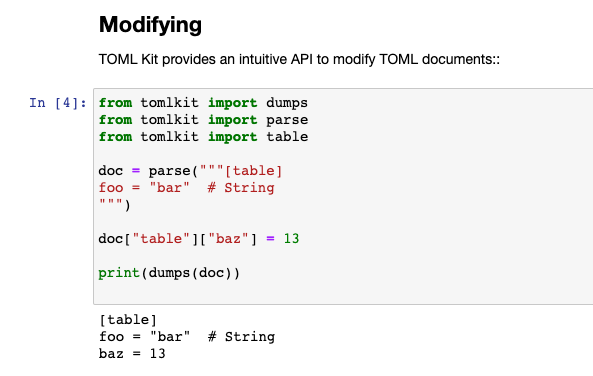
You can find the enhanced tomlkit fork on github.
Happy coding!

Comments